Blockchain technology underpins digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. A blockchain is essentially a catalog of transactions that anybody can examine and validate. For instance, the Bitcoin blockchain keeps track of every time someone sends or receives bitcoin. Online value transfers are made possible by cryptocurrencies and the blockchain technology that underpins them, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks or credit card companies.
- Blockchain networks provide security for almost all cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash, and Litecoin. Which implies that a significant amount of computational power is constantly used to verify their accuracy.
- For the majority of cryptocurrencies, the blockchain’s record of transactions is essential because it enables secure payments to be conducted between strangers without going through a third-party validator like a bank.
- Blockchain-based payments have the potential to be more secure than traditional debit/credit card transactions because of the networks’ cryptographic architecture. For instance, you don’t have to give any private information while paying with Bitcoin. Your chance of having your bank information exposed or having your identity stolen is therefore essentially zero.
The fact that blockchain technology is useful outside cryptocurrencies makes it even more exciting. Blockchain technology is being used for a variety of purposes, including medical research, enhancing the accuracy of medical data, streamlining supply networks, and much more.
What are some blockchain benefits?
Because they are international, bitcoins may be swiftly and inexpensively sent around the world.
They promote privacy because you can avoid identity theft and hacking by using cryptocurrency payments without disclosing any personal information.
They are open Anyone can examine bitcoin networks’ transactions because every single one is disclosed openly in the form of the blockchain. That eliminates the possibility of manipulating transactions, altering the money supply, or changing the rules in the middle of a game. Anyone can examine the source code of the free and open-source software that forms the foundation of these currencies.
Key inquiries
What distinguishes blockchain technology from the legacy financial system?
Consider how much of your financial life is conducted online, from investing to buying, and how each and every one of those transactions necessitates the involvement of a bank, credit card provider, or payment processor like Paypal. These transactions may now be carried out without a middleman and without the extra expenses and complexity that go along with them thanks to blockchain technology.
Bitcoin: Is it a blockchain?
A type of digital money is bitcoin. A blockchain is the enabling technology that makes it feasible.
How many different types of blockchains exist?
thousands, ranging from those that power digital currencies like Bitcoin, Litecoin, Tezos, and countless others to an increasing number of people with nothing.
The way a blockchain functions?
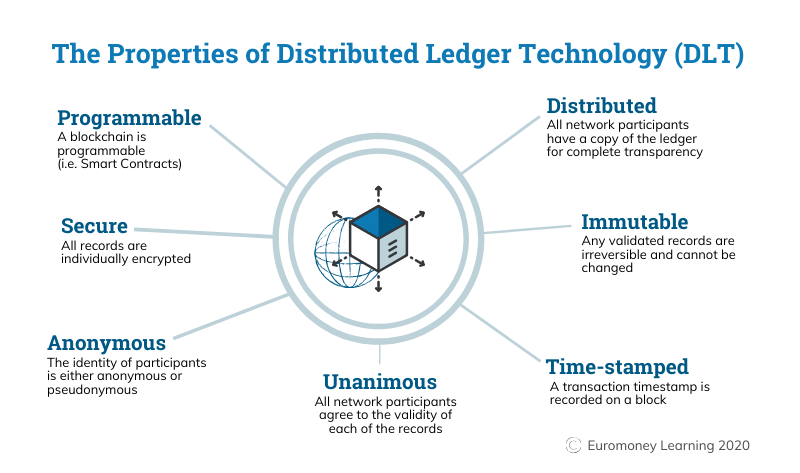
Think of a chain that might be used as a ship’s anchor. But in this instance, each link in the chain is a unit of data that includes transaction information. The most recent transactions appear at the top of the chain, and as you descend the chain, you see progressively older transactions.
What happens if you follow it all the way to the anchor that is anchored at the harbor’s bottom? You will be familiar with every single transaction in that cryptocurrency’s past. Due to the blockchain’s openness and transparency in recording a cryptocurrency’s full history, it has strong security advantages. Any attempt to interfere with a transaction will result in the link breaking, which will be visible to the entire network.
Another way that the blockchain is sometimes described is as a ledger that resembles a bank’s balance sheet (also referred to as a “distributed ledger” or “immutable ledger”). The blockchain keeps track of all the money moving into, out of, and through the network just like a bank’s ledger would.
However, unlike a bank’s books, no one or institution, not even banks or governments, maintains a crypto blockchain. It isn’t centralized at all, in reality. Instead, a sizable peer-to-peer network of machines running open-source software serves as its security system. The blockchain’s accuracy is continually monitored and secured by the network.
From where do new cryptocurrencies originate? A new piece of transaction data, or a new block, is periodically added to the chain of existing data—roughly every 10 minutes in the case of Bitcoin. The network pays participants a tiny amount of digital currency in return for using their processing resources to help maintain the blockchain.
A crypto blockchain is dispersed throughout the network of the digital currency. It is not governed by any corporation, nation, or other entity, and anybody can take part.
Who was the blockchain’s inventor?
In late 2008, a person or group going by the moniker Satoshi Nakamoto posted a whitepaper online outlining the fundamentals of a brand-new digital currency named Bitcoin. Since then, every cryptocurrency has evolved from the concepts presented in that paper.
The purpose of Nakamoto’s digital currency was to enable internet transactions between strangers anywhere in the globe without the need of a middleman, such as a credit card company or payment processor like Paypal.
This called for a method that would get rid of the tricky problem of “double spending,” in which someone might spend the same money more than once. A network that continuously verifies Bitcoin transactions is the answer.
Beyond the control of any one person, organization, or nation, a worldwide network of computers stores and verifies each Bitcoin transaction.
The blockchain is the name of the database that houses all of that data. The vast, decentralized (also known as peer-to-peer) computer network that is continuously ensuring the accuracy of the blockchain is used to “mine” bitcoins. Miners receive modest sums of cryptocurrency in return for using their computational power to contribute to the blockchain.
Every single bitcoin transaction is recorded on the ledger. New data is regularly collected into a “block,” which is then added to all previous blocks.
What is blockchain technology’s future?
The concept of a blockchain has proven to be a platform on which a wide variety of applications can be created. Although blockchain is still a young and fast evolving technology, many experts have compared its potential to revolutionize how we live and work to the potential that early public internet protocols like HTML had for the World Wide Web.
The operation of the blockchains for Bitcoin Cash and Litecoin is strikingly similar to that of the original Bitcoin blockchain. The Ethereum blockchain, in contrast to the Bitcoin blockchain, is not only intended to maintain a digital currency, hence it represents a further development of the distributed ledger concept.
(Having said that, Ethereum is a cryptocurrency and may undoubtedly be used to pay money to someone else.) Consider the Ethereum blockchain as more of a robust and highly adaptable computing platform that enables programmers to quickly create various blockchain-based apps.
Consider a charity that wants to donate money to 1,000 people each day for a year. That would only require a few lines of code in Ethereum.